Introduction
Modern packaging lines serve multiple critical functions in manufacturing. First, they enhance efficiency significantly. Second, they reduce costs effectively. Third, they ensure consistent product quality. Moreover, well-designed packaging lines help meet diverse market demands.
However, building efficient packaging lines involves complex processes. Additionally, careful planning becomes essential for success. Furthermore, equipment selection requires expert knowledge. From conceptual design to actual operation, multiple challenges arise.
This comprehensive guide covers all essential aspects of packaging line construction. Moreover, it provides practical insights from requirements analysis to implementation strategies.
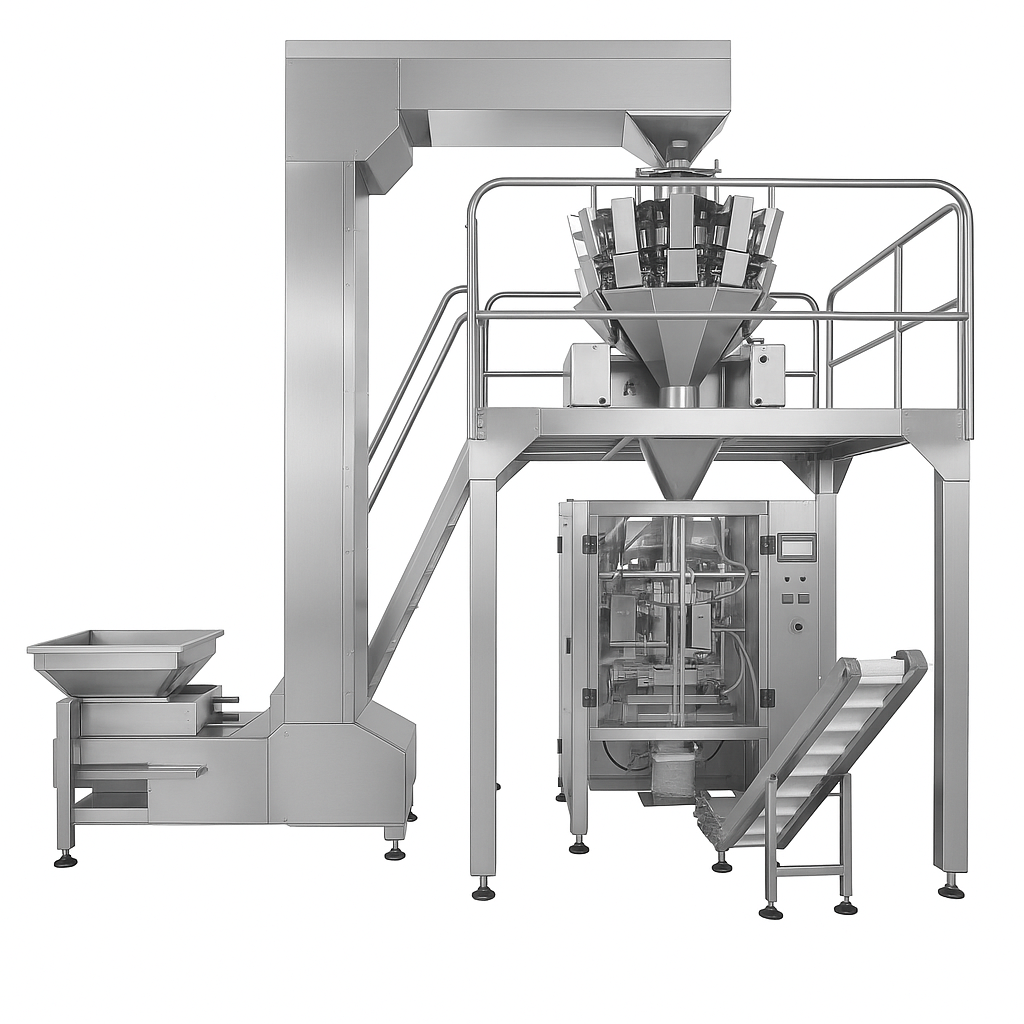
1. Requirements Analysis: Defining Your Packaging Objectives
Thorough requirements analysis forms the foundation of successful projects. Therefore, close collaboration with multiple departments becomes necessary. Specifically, production, marketing, sales, and quality control teams must participate actively.
Understanding project objectives requires a comprehensive assessment. First, evaluate product specifications carefully. Next, analyze packaging materials thoroughly. Additionally, consider production goals realistically. Finally, assess budget constraints honestly.
•Product Specifications: Understanding product characteristics is crucial for equipment selection. For instance, physical dimensions affect conveyor requirements. Moreover, weight influences handling systems. Additionally, fragility determines protection needs.
•Packaging Formats: The Final product presentation affects consumer appeal directly. Therefore, determine packaging forms early in planning. Furthermore, material type selection impacts equipment specifications.
•Production Volume and Speed: Expected capacity drives equipment selection decisions. Moreover, hourly output requirements influence line speed. Additionally, shift patterns affect automation needs.
•Regulations and Compliance: Industry-specific requirements must be considered carefully. For example, food safety standards affect equipment design. Furthermore, pharmaceutical regulations influence material selection.
2. Core Design Elements: Building Blocks of Packaging Lines
Efficient packaging lines consist of interconnected systems working harmoniously. Therefore, focus on several core elements during design phases.
2.1 Layout Configuration
Physical layout directly impacts operational efficiency. Moreover, proper design minimizes transport distances. Additionally, it reduces potential bottlenecks effectively. Furthermore, optimized layouts improve operator workflows.
Common layout types offer different advantages [2]:
•Linear Layout: This arrangement suits high-volume production best. Moreover, it works well for single-product operations. Additionally, equipment placement follows sequential order.
•U-shaped Layout: Space-limited facilities benefit from this design. Furthermore, it maximizes available floor space. Additionally, it provides operational flexibility.
•L-shaped Layout: This configuration handles workflow interruptions effectively. Moreover, it accommodates inspection points easily. Furthermore, it offers design flexibility.
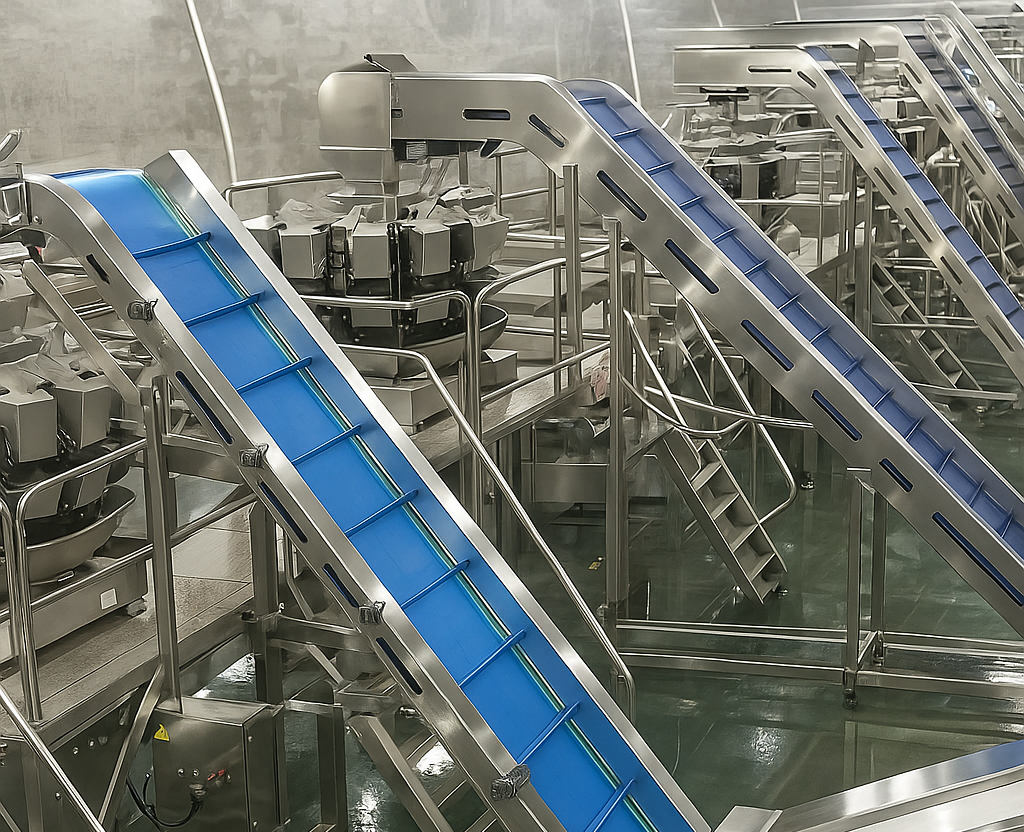
2.2 Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems connect various packaging line components effectively. Therefore, selecting appropriate types becomes crucial. Moreover, product characteristics influence conveyor selection significantly.
Different conveyor types serve specific purposes [2]:
•Belt Conveyors: These systems handle lightweight products effectively. Moreover, they accommodate fragile items safely. Additionally, they work well with irregular shapes.
•Roller Conveyors: Heavy products benefit from roller systems. Furthermore, flat-bottomed items move efficiently on rollers. Additionally, they provide reliable transport.
•Chain Conveyors: Precise positioning becomes possible with chain systems. Moreover, they enable automated operations effectively. Furthermore, they handle heavy loads reliably.

2.3 Packaging Equipment
Equipment selection depends on specific product and packaging requirements. Therefore, careful evaluation becomes necessary. Moreover, integration capabilities must be considered.
Essential equipment categories include several types:
•Weighing Systems: Multihead weighers ensure measurement accuracy. Moreover, industrial scales provide reliable performance. Additionally, they integrate with control systems effectively.
•Filling Equipment: Auger fillers work well for powders. Meanwhile, piston pumps suit liquid applications. Furthermore, VFFS machines handle multiple product types.
•Sealing Equipment: Package integrity depends on proper sealing. Moreover, consistent sealing ensures product protection. Additionally, it affects shelf life significantly.
2.4 Quality Assurance
Quality systems ensure products meet established standards. Therefore, integration becomes essential for success [2].
Key quality components include:
•Vision Systems: These detect product defects automatically. Moreover, they verify packaging integrity. Additionally, they check label accuracy.
•Check Weigher: Fill accuracy verification becomes automated. Furthermore, they ensure consistent product weights. Additionally, they reduce giveaway costs.
•Metal Detectors: Contamination prevention protects consumers. Moreover, it maintains brand reputation. Furthermore, it ensures regulatory compliance.
3. Automation Integration: Enhancing Efficiency and Reliability
Automation represents the core of modern packaging lines. Moreover, it provides multiple operational benefits. First, labor costs decrease significantly. Second, human errors reduce substantially. Third, production efficiency improves dramatically [2].
•Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): These serve as packaging line “brains.” Moreover, they coordinate all equipment operations. Additionally, they enable centralized control.
•Human Machine Interface (HMI): Intuitive control platforms improve operator efficiency. Furthermore, they provide real-time monitoring capabilities. Additionally, they simplify parameter adjustments.
•Robotic Automation: Robots handle repetitive tasks effectively. Moreover, they improve positioning accuracy. Furthermore, they increase operational flexibility.
4. Implementation Strategy: From Planning to Operation
4.1 Supplier Selection and Collaboration
Choosing experienced suppliers is crucial for project success. Moreover, reputation and track record matter significantly. Additionally, technical support capabilities require evaluation.
Establishing close partnerships ensures project success. Furthermore, suppliers must understand requirements completely. Additionally, they should provide comprehensive support services.
4.2 Layout Optimization and Simulation
Simulation software enables layout optimization before installation. Moreover, it identifies potential bottlenecks early. Additionally, 3D modeling helps visualize equipment placement .
Virtual testing reduces implementation risks significantly. Furthermore, it optimizes operator pathways. Additionally, it ensures optimal working environments.
4.3 Testing and Commissioning
Comprehensive testing ensures proper operation before production. First, individual machine testing verifies functionality. Next, integrated testing confirms system coordination. Finally, production testing validates performance.
4.4 Training and Maintenance
Adequate training ensures operational success. Moreover, operators must understand the equipment thoroughly. Additionally, maintenance personnel need technical knowledge.
Preventive maintenance plans minimize unexpected downtime. Furthermore, they extend equipment lifespan. Additionally, they reduce operational costs.
Conclusion
Building efficient packaging lines requires careful planning and execution. However, proper approach yields significant competitive advantages. Through systematic analysis and wise equipment selection, success becomes achievable.
Investment in modern packaging lines benefits multiple areas. First, production efficiency improves substantially. Second, product quality becomes more consistent. Third, brand reputation strengthens significantly. Ultimately, these improvements drive future enterprise growth.

