Introduction: The Versatile Workhorse of Industrial Plastics
In the world of industrial machinery, the focus is often on steel, aluminum, and other metals. However, a quiet revolution has been taking place, led by high-performance engineering plastics. At the forefront of this revolution is the humble Varilla de nailon . For machine manufacturers, it represents a powerful tool for designing lighter, quieter, and more efficient equipment. For parts wholesalers, it is a high-demand, versatile stock item that solves countless customer problems.
From acting as a low-friction wear strip on a high-speed transportador to being machined into a custom gear, the nylon rod is a cornerstone of modern mechanical design. Its unique combination of properties—strength, low friction, and wear resistance—allows it to replace metal in many applications, delivering superior performance and a lower total cost of ownership. This guide will explore the critical role of nylon rods, particularly in sistemas transportadores, and provide the expert insights needed to select the right material and design for your needs.
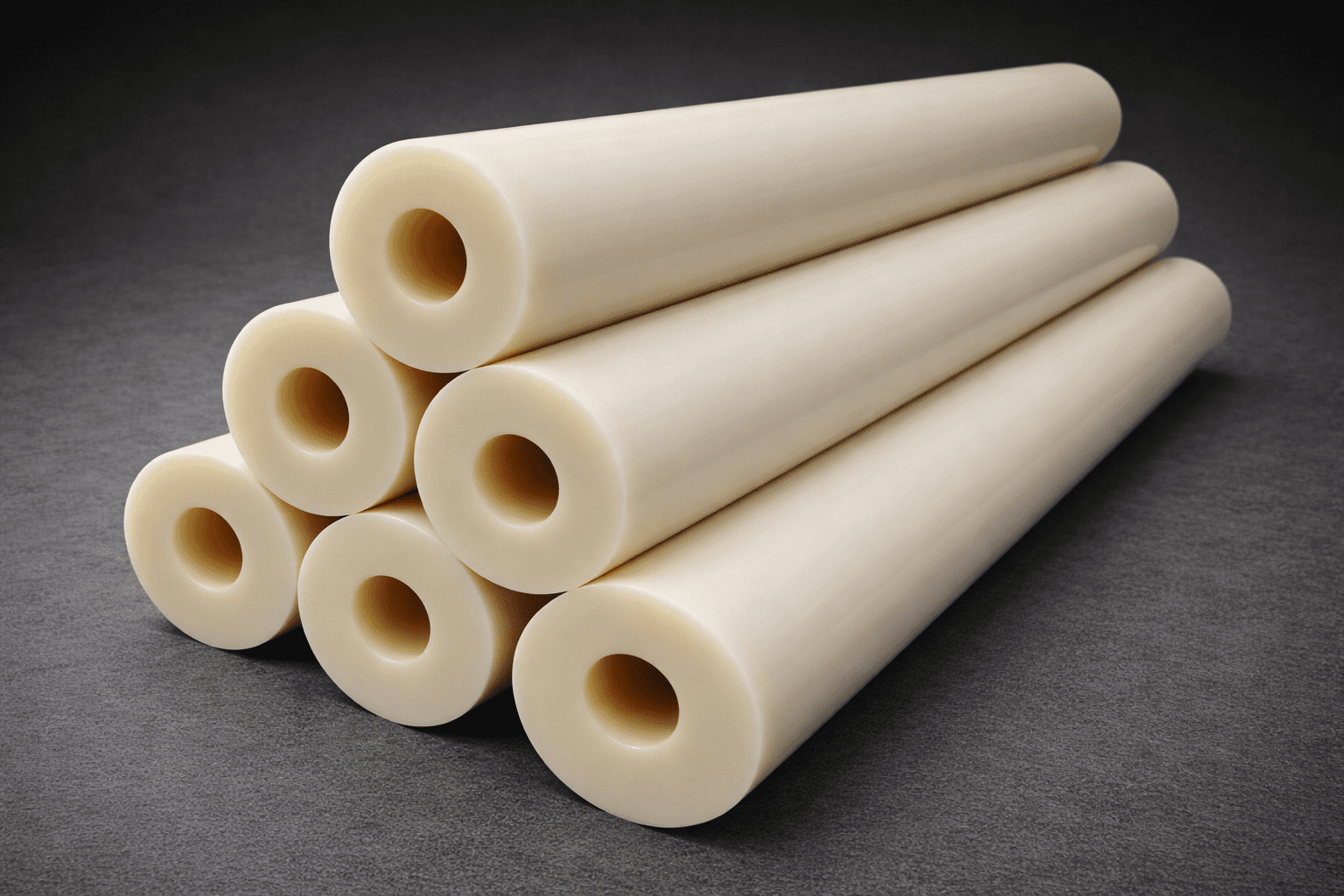

Part 1: The Critical Role of Nylon Rods in Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems are the arteries of modern production, and their reliability is paramount. Nylon rods are essential components that ensure these systems run smoothly, quietly, and with minimal maintenance. Their primary functions include:
- Wear Strips and Chain Guides: This is one of the most common applications. Placed along the path of a conveyor chain or belt, nylon rods provide a smooth, low-friction surface for the chain to glide on. Because nylon is self-lubricating, it drastically reduces the energy required to drive the system and eliminates the need for external lubrication, which is critical in clean environments like food processing.
- Belt and Product Support: In long conveyor spans, nylon rods can be used as support rollers or fixed supports under the belt. Their smooth surface prevents damage to the belt, and their inherent strength allows them to support significant weight without deforming.
- Side Guides and Bumpers: Used along the edges of a conveyor, nylon rods gently guide products, preventing them from falling off or jamming. Their natural impact resistance allows them to absorb repeated bumps without cracking or damaging the products.
Part 2: Material Deep Dive: Cast Nylon vs. Nylon 66
Not all nylon is created equal. The two most common types used in industrial applications are Cast Nylon (PA6G) y Extruded Nylon 66 (PA66). Choosing the right one is critical for performance.
Característica | Cast Nylon (PA6G) | Nylon 66 (PA66) |
Manufacturing Process | Liquid monomer is poured into a mold and polymerized. | Molten polymer is forced through a die (extruded). |
Mejor para | Large, heavy-duty components. Gears, large rollers, and high-load wear pads. | Smaller, high-precision parts. Bushings, intricate components, and applications requiring higher temperature resistance. |
Compressive Strength | Higher. Its crystalline structure gives it superior load-bearing capability without deforming. | Lower. More suited for moderate loads. |
Wear Resistance | Excelente. One of the most wear-resistant thermoplastics available, ideal for high-friction applications. | Very Good. Offers good wear resistance, but generally less than cast nylon. |
Thermal Stability | Good. Suitable for most standard operating temperatures. | Higher. Can operate at a higher continuous temperature, making it better for applications near motors or other heat sources. |
Hardness & Stiffness | Hard and Tough. A good balance of hardness and impact resistance. | Harder and Stiffer. Less flexible than cast nylon, which can be an advantage for maintaining tight tolerances. |
Regla de oro: For large-diameter rods (>100mm) or applications involving very high loads and abrasion, choose Cast Nylon. For smaller, more intricate parts or those exposed to higher temperatures, Nylon 66 is often the better choice.
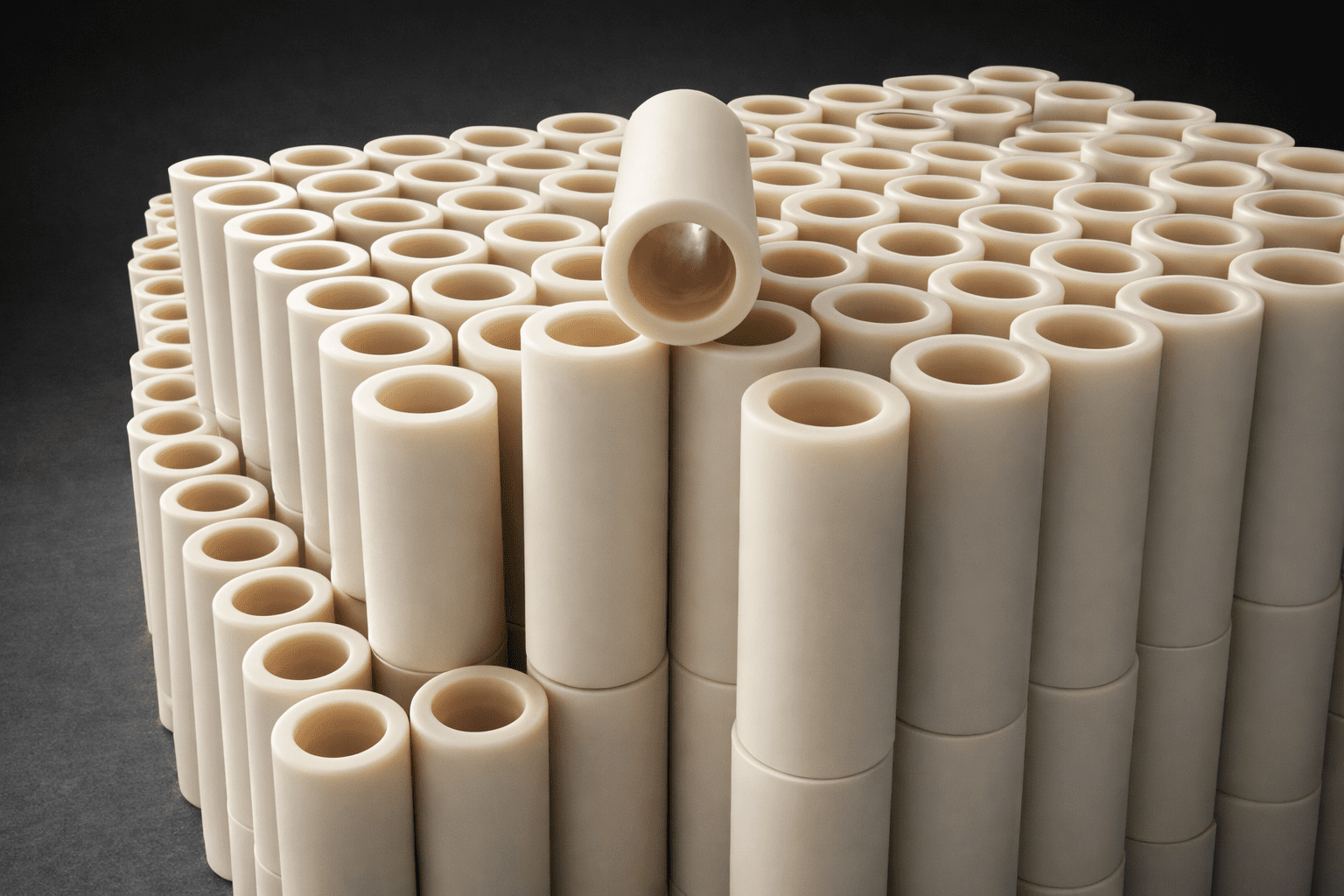
Part 3: The Hollow Advantage: Why Tubes Outperform Solid Rods
The image you provided shows a hollow nylon rod, or tube. While solid rods have their place, the hollow format offers a powerful set of engineering and cost benefits that are often overlooked.
- Significant Weight Reduction: A hollow rod has an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This reduces the overall inertia of a conveyor system, leading to lower energy consumption and allowing for faster acceleration/deceleration. It also makes the parts easier and safer to handle during installation and maintenance.
- Superior Cost-Effectiveness: You are only paying for the material you need. Hollow rods use significantly less raw material, which translates to lower purchasing and shipping costs. For parts that will be machined into a final component with a hole (like a bushing or roller), starting with a hollow rod dramatically reduces machining time and waste.
- Enhanced Flexibility: The tubular structure allows for a degree of flexibility, making hollow rods ideal for creating curved guide paths for belts or chains—a task that is difficult to achieve with solid rods.
Part 4: An Engineer’s Guide to Selection
For machine manufacturers, selecting the right nylon rod specification is key to performance.
- Define the Function: Is the rod a simple wear strip, a load-bearing roller, or a precision-machined gear? The function will be the primary driver of your material and size choice.
- Analyze the Load and Speed: High loads and abrasive conditions favor Cast Nylon. High speeds and the need for tight tolerances may favor Nylon 66. Calculate the forces involved and choose a diameter and wall thickness (for hollow rods) that can handle the stress with an appropriate safety factor.
- Assess the Environment: Consider the operating temperature and any chemical exposure. While all nylon is resistant to oils and greases, specific chemicals may require a particular grade. Ensure your choice meets the thermal demands of the application.
Part 5: A Wholesaler’s Corner: Stocking for Profit
For parts wholesalers, nylon rod is a versatile, high-turnover product. A smart inventory strategy is crucial.
- Stock the Core Sizes: Focus on the most common diameters used in conveyor and general machine building, typically ranging from 20mm to 100mm.
- Offer Both Solid and Hollow: While solid rods are traditional, promoting the cost and weight benefits of hollow rods can make you a more valuable supplier to your customers.
- Carry Both PA6G and PA66: Stocking small-diameter Nylon 66 rods and larger-diameter Cast Nylon rods allows you to cover the majority of customer applications.
- Provide Cut-to-Length Services: Offering to cut rods to a customer’s specific length is a simple value-add service that can set you apart from the competition and generate additional revenue.
Conclusion: The Smart Replacement for Metal
Nylon rod is more than just a plastic bar; it is a sophisticated engineering material that enables the design of lighter, quieter, more efficient, and longer-lasting machinery. Its application as a wear strip, guide, or support in conveyor systems is a perfect example of its ability to outperform metal in key areas. For machine builders, embracing nylon is an investment in innovation. For wholesalers, it is an essential, profitable, and problem-solving product line.
Ready to leverage the power of high-performance nylon in your next project? Contact us today for expert material selection advice, custom sizing, and a competitive quote.

